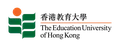As a Malaysian, you’ve probably heard words exchanged about our neighbour, Singapore. At the same time, one cannot deny the impact Singapore has and the influence the country holds on not just Asia, but the world.
Curious about higher education in Singapore? We've got just the guide for you.
What’s in Singapore?
Singapore is one of the most competitive, safest, and innovative cosmopolitans and financial hubs in the world.
Additionally, two of its public universities – Nanyang Technological University (NTU) and National University of Singapore (NUS) – are ranked top 3 in Asia and top 10 in the world. This attracts students from all over the world to enrol in Singapore’s universities and earn a world-class degree, ranking alongside other elite institutions in the UK.
As a Malaysian student, Singapore wouldn't be much of a culture shock for you. Nevertheless, studying in Singapore would still be a new experience.
We also find that language isn’t a barrier, as it often is with Asian countries; English is heralded as the national language, along with Mandarin, Tamil and Malay. So, as a Malaysian, you wouldn't have much to worry about!
While Singapore may, however, be a relatively expensive city to reside in compared to Malaysia, several measures are taken by the government to allow for an easier and more convenient lifestyle: 80% of it’s population resides in government-subsidised housing and the use of public transportation is encouraged by the government as well.
Top Universities in Singapore
In the Programme for International Assessment (Pisa) in 2016, it was found that children from Singapore are amongst the best in the world for Maths, Science and Literacy Skills.
With a solid foundation in primary and secondary schooling years, it’s easy to see why Singapore’s universities consistently out-perform many of the world’s institutions; not only in ranking but quality in teaching, research and facilities, among several other factors.
With more than 50,000 international students enrolling in Singaporean universities annually, competition tends to be high. The most popular and highly-ranked institutions are as below:

Semester breaks, especially during summer are an ideal chance for students to search for part-time jobs or internships as well. This gives the extra boost to your resumes upon graduation – and some extra cash in your pockets! Universities and colleges in Singapore typically follow a two-semester format, whereby 1st semesters commence in August annually, with a winter break between December and January of the following year, after which the 2nd semester commences and ends in May, followed by a semester breakthrough to July.

While NUS and NTU are amongst the most popular of institutions in Singapore, other institutions provide students with many choices, both in qualification and type of degrees obtained.
This means many institutions in Singapore also offer overseas degrees to students without them having to leave the country through partner institutions. Singapore’s higher education institutions can be profiled as the following:
1. Public Universities
Although they receive government funding, they are autonomous – meaning they can strategise, innovate, and differentiate themselves as they pursue excellence in education, research, and service. Example: National University of Singapore (NUS) and Singapore Management University (SMU).
2. Private Universities
Although privately funded, these institutions receive government funding for students to pursue subsidised part-time or full-time degrees. Example: Singapore University of Social Sciences (SUSS, formerly known as SIM University).
3. Polytechnic Institutions
These offer practice-oriented studies at diploma level and are key providers of continuing education and post-employment professional development services. Example: Nanyang Polytechnic and Ngee Ann Polytechnic.
4. Institute of Technical Education (ITE)
The ITEs offer technical-oriented studies and help to develop technical knowledge and skills of their students. Here, students are provided with the option of choosing between full or part-time educational or traineeship courses. Example: TITE College and ITE College East.
5. Foreign Universities
With branch campuses in Singapore, these universities offer undergraduate and postgraduate degrees. Example: INSEAD Asia Campus and James Cook University Singapore.
6. Art Schools
These institutions act as schools that offer specialist creative education to enhance students’ artistic ability. Example: The Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts (NAFA) and LASELLE College of the Arts (LASELLE).
Students are generally advised to choose their institution based on their own preference and field of study.
Did you know? Singapore ranks as the 17th best Student City in the world based on QS University Rankings as of 2021.
What to study in Singapore?
Some of the most popular courses in Singapore are Law, Medicine, Accounting, Information Technology and Communication Studies. In addition, we've prepared lists of universities in Singapore grouped by subject:
- Universities for MBA
- Universities for Business
- Universities for Law
- Universities for Engineering
- Universities for Creative Arts
Entry Requirements
Prior to choosing the right university, it is crucial to ensure that you are capable of meeting the entry requirements and tuition fees of the university. Do note that Singaporean universities, while placing high in global rankings, are extremely competitive and can have relatively expensive tuition fees as well.
However, scholarships are often readily available – particularly to Malaysians and other ASEAN nationals – and can be a convenient solution to this.
Academic Entry Requirements
Generally, academic entry requirements differ according to the course a prospective student wants to apply for, as well as the institution they hope to enrol in. For a Bachelor’s Degree course in Singapore, Malaysian students must have completed the following academic qualifications:
- SPM (Form 5) or UEC: Minimum of 4 passes
- STPM: Minimum of 2 passes
- O-Level and A-Level (or equivalent): Minimum of 3 O-Level passes and 2 A-Level passes
Some courses require students to complete their pre-university qualification in specific subjects. For example, if you wish to study Engineering, Maths should be taken up and completed during your pre-university.
Language Entry Requirements
As the English Language is the medium of instruction in Singaporean universities and colleges, it is required for students to have completed an English Proficiency test prior to applying for a course. Minimum grades usually depend on the course and institution, but average language entry requirements include a minimum:
- Overall 6.0 - 6.5 in the International English Language Testing System (IELTS)
- Overall 100 in the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL)
- Overall 68 in the Pearson Test of English (PTE Academic)
- Overall 200 in the Malaysian University English Test (MUET)
Tuition Fees
Cashing in on your future tend to be pricey, more so in a country like Singapore. However, students are encouraged to search for scholarships, many of which are readily available for Malaysian students. General tuition fees per year at Singaporean universities for various qualifications are listed as below.
| Study level | SGD | MYR |
| Foundation / Pre-U | 12,000 - 18,000 | 36,000 - 55,000 |
| Diploma | 5,000 - 18,000 | 15,000 - 55,000 |
| Bachelor's degree | 20,000 - 60,000 | 60,000 - 182,000 |
| Master's degree | 30,000 - 90,000 | 91,000 - 274,000 |
| PhD | 20,000 - 90,000 | 60,000 - 274,000 |
*Tuition prices in MYR are subject to conversion from SGD
Living Costs
Having been voted under the 10 most expensive cities in Asia, Singapore can be quite a leap if you’re coming from Malaysia. If you tend to have the habit of constantly converting between currencies in your head while residing in a new country, the Singaporean dollar may seem like a far stretch from the Malaysian ringgit.
While Singapore may be an expensive city to reside in, it ranks as one of the best places in Asia to live in as well. A financial hub and multinational hub for not just Asia but the world, Singapore can be a treat to live in where students gain plenty of exposure to Asian and Western cultures.
When it comes to living costs in Singapore, much of students’ monthly expenditure depends on the student and their preferred lifestyle.
| Expense category | SGD/month | MYR/month |
| Student accommodation | 200 - 800 | 600 - 2,400 |
| Transport, monthly pass | 100 - 120 | 300 - 365 |
| McDonald's combo meal | 8 | 24 |
| Simple meal in a foodcourt | 6 - 10 | 18 - 30 |
Did you know? Full-time students in Singapore are entitled to concessions while using the MRT!
For students looking to combat their monthly expenses, the Immigrations and Checkpoints Authority (ICA) in Singapore allows for international students to seek part-time work: 16 hours per week during the academic term and an unrestricted number of hours during term vacations.
Not only does this give students the independence of not having to fully rely on their parents, but it too helps to boost students’ resumes upon graduation.
Application & Visa Requirements
The following illustration shows the high-level process of applying to universities in Singapore. For specific details please contact EasyUni.
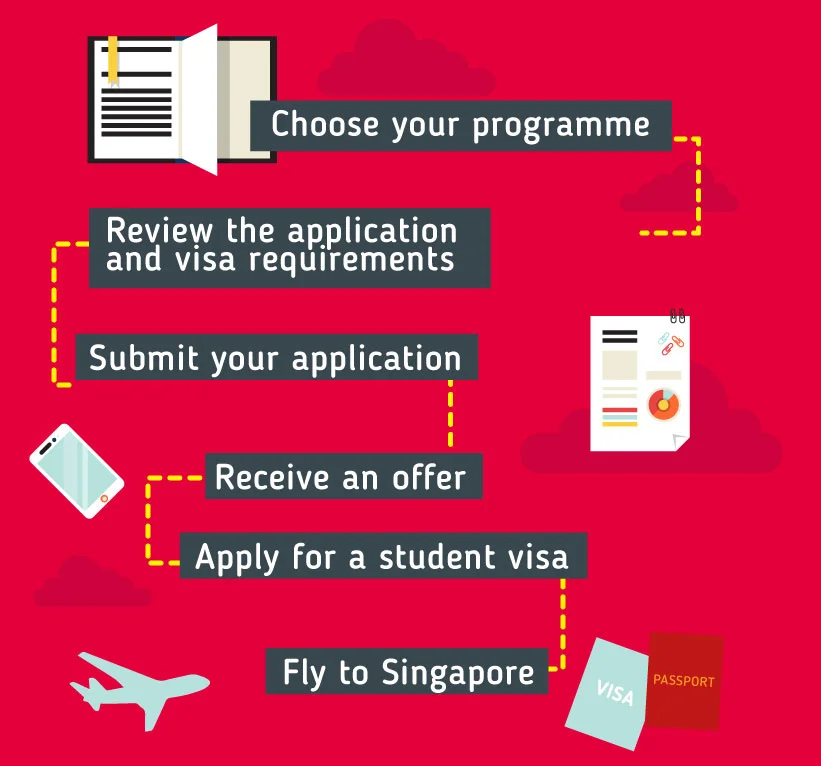
After having met the entry requirements and decided on which university in Singapore you wish to attend, students must begin their course application.
When to apply to Singapore?
If you’re looking to enrol in an undergraduate course in Singapore, it is best to apply as early as possible. Students are encouraged to apply using forecast results if available, instead of waiting for their pre-university results and losing out on a particular admission date or semester.
For example, if you’re considering applying to a course which resumes in August, start applying for your chosen Singaporean university starting February that year – or even earlier!
For Malaysian students, obtaining a student pass is an integral part of the application process. Without it, you won’t be a registered student in Singapore. Once you are accepted into your university of choice, your student visa will be applied for by the university itself.
However, you must apply for a Student Pass from the Immigration & Checkpoints Authority (ICA) 1 to 2 months before the start of your course. You need to have the information provided by your university after acceptance, and submit:
- eForm 16
- Passport details
- Your university’s address
- Your email address
- A passport sized photo
Following your arrival in Singapore, you would be required to visit the ICA for the collection of your Student Pass, inclusive of a fee of S$60.
Student Life
Coming from Malaysia, student life in Singapore would be comparatively different. While Malaysia averages an area of 330,803 km2, Singapore’s area rounds up to a small 719.9km2. However, a difference in area doesn’t necessarily mean a lack of opportunities.

While Singapore may not be home to islands, mountains and rainforests, its appeal lies in its modernity and urbanisation. Singapore offers students a life of luxury; work hard, play hard is the ethic and, during days off, students can spend their time exploring the nooks and crannies or branching out to spend the weekends at the infamous Resorts World Sentosa, one of Asia’s top attractions harbouring a little something for everyone – including Universal Studios!
After-Graduation Opportunities in Singapore
Completing your studies in Singapore offers a multitude of options concerning what’s next, instead of merely returning home to Malaysia upon graduation.
Extend your studies
Whether you chose to pursue a Pre-University course, Diploma or Degree in Singapore, there’s always the possibility of being one step ahead. Many prefer continuing their studies after wrapping up their Degree or Diploma, such as pursuing a Master’s or PhD at one of the many elite institutions in Singapore.
Obtain a long-term visit pass
Intrigued to continue staying in Singapore after graduating? Malaysian students who wish to stay in Singapore for a while longer, whether for leisure of to find work are allowed to apply for a long-term visit pass. This pass enables international students to continue residing in the country for up to 12 months. Students can find out more about this on the official ICA website.
In order to apply for a long-term visit pass, ensure that your student pass is valid for another 10 days, at the very least. Otherwise, graduates will not be allowed to apply for the pass.
Seek employment
Working in one of the biggest and most innovative hubs of Asia pushes students to make the most out of their careers. While the job market may be tough, it is only due to the high rate of competitiveness. However, if you do manage to obtain a job in Singapore, your career may just get the head start it needs!
Did you know? Once you begin earning a minimum of SGD3,000 (MYR8,900) monthly, you are also eligible to apply for a Singaporean Permanent Residence (PR) pass.
Return home
So you’ve finished your studies in Singapore and wish to head back home for employment because, after all, Malaysia boleh! Before you pack up and head back, however, do ensure that your bills, accommodation and other possessions are all taken care of. Concerning your degree certificate, graduates must collect it and any other relevant documents from their university before leaving the country as well.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get scholarships to study at Singapore?
Singapore offers scholarships to students for various levels of education and programs. For each scholarship, the requirements are different. Get access to the available scholarships here.
Can I work while studying in Singapore?
With a Work Pass Exemption, International students are allowed to work a maximum of 16 hours per week in Singapore.
 +60142521561
+60142521561